Anatomy of a flipped classroom
A well-designed flipped course requires a significant amount of planning and preparation, but has great benefit to both students and instructor. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy as a guide, one can design effective online and in-class components that maximize benefits to students. A flipped classroom allows students more time to interact with peers and their teacher, and collaborate with teams. This paper will describe how one tourism educator flipped an advanced marketing course, as well as the technology tools used in content creation.
Flipped Classrooms 2.0
Though some instructors think flipping the classroom is as simple as students watching
lectures online and doing their homework in class, version 2.0 of the practice is evolving to allow faculty to provide more rigorous, in-depth instruction.
Flipped classroom experiences: student preferences and flip strategy in a higher education contex
Despite the popularity of the flipped classroom, its effectiveness in achieving greater engagement and learning outcomes is currently lacking substantial empirical evidence. This study surveyed 563 undergraduate and postgraduate students (61 % female) participating in flipped teaching environments and ten convenors of the flipped courses in which the student sample was enrolled. Results suggest that higher education students can be differentiated based on their preferences for elements of a flipped classroom, resulting in two clusters of students: those who embrace most aspects of a flipped classroom environment as well as prefer it (labelled ‘‘Flip endorsers’’) and those who are close to neutral on some elements of a flipped classroom environment but who especially do not endorse the pre-learning aspects (labelled ‘‘Flip resisters’’).
Evaluating the flipped VS traditional teaching method on student nurse's performance.
Recent advances in technology have unlocked entirely new directions for education research. Educators have been working to break the lecture centered instruction model by shifting the focus from the curriculum pacing guide to student learning needs such as flipped learning i.e. shifting direct learning instructional outside the group learning space to the individual learning space.
What Do I Do with this Flipping Classroom: Ideas for Effectively Using Class Time in a Flipped Course
Flipping the classroom is an increasingly popular teaching style, but converting a class to a flipped format can be challenging. Apart from creating or finding the external resources that will take the place of traditional lectures,
instructors must also find ways to use classroom time. We describe ideas and suggestions for effectively using class
time to improve students learning.
Questions to consider before flipping
Flipping the classroom is one of the hottest new educational ideas that promises to increase student engagement. However, recent research suggests that not all content areas are equal when it comes to flipping. English language arts and humanities-based subjects may not benefit as much as math and science classes and, in fact, decrease student engagement. The authors posit five key questions that teachers and administrators should consider before advocating a flipped classroom approach.
Student and Instructor Perceptions of a Flipped College Algebra Classroom
Each year about half a million students fail to make planned academic progress due to college algebra, hence the need for researchers to find ways of improving the quality of instruction in the course. Recent research suggests that flipping college algebra to allow time for active learning in the classroom may improve student performance. Also, the costs of college textbooks have skyrocketed in the last few years, preventing or discouraging students from obtaining crucial learning resources. To address both concerns, the researcher implemented a flipped college algebra classroom and based all lessons on a free textbook. Videos and corresponding problem sets were created and made available to students on the Internet. Outside class, students viewed videos, took notes, and completed video problem assignments. Inside class, students worked with other students to complete in-class problem assignments. Students described their experience in the flipped classroom in an anonymous essay and an online survey, and the researcher recorded field notes of his observations throughout the term. This study reports student and instructor perceptions of the flipped college algebra classroom.
Exploring the Flipped Classroom in a Community College Setting
The purpose of this study was to explore the flipped classroom approach in a community college setting and assess its impact on students’ learning experience and performance.
Student experiences across multiple flipped courses in a single curriculum
The flipped classroom approach has garnered significant attention in health professions education, which has resulted in calls for curriculum-wide implementations of the model. However, research to support the development of evidence-based guidelines for large-scale flipped classroom implementations is lacking. Objectives This study was designed to examine how students experience the flipped classroom model of learning in multiple courses within a single curriculum, as well as to identify specific elements of flipped learning that students perceive as beneficial or challenging.

 Image: https://www.nea.org/professional-excellence/professional-learning
Image: https://www.nea.org/professional-excellence/professional-learning 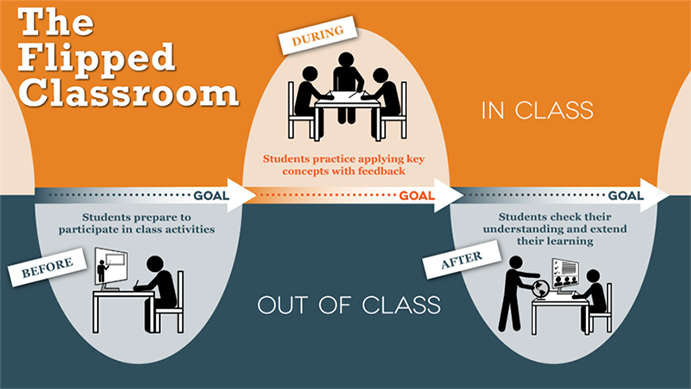
 Teaching at its best : a research-based resource for college instructors by Linda Nilson
Teaching at its best : a research-based resource for college instructors by Linda Nilson